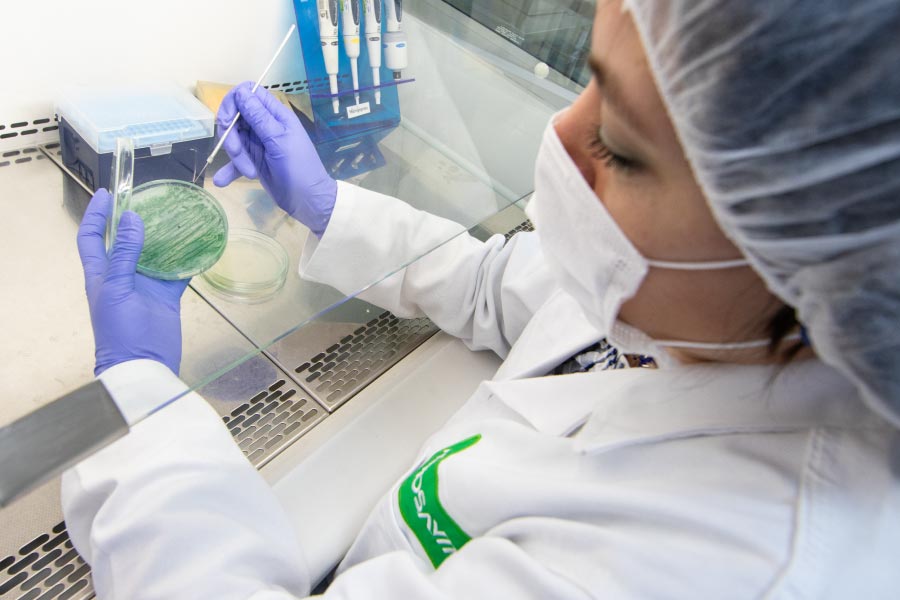
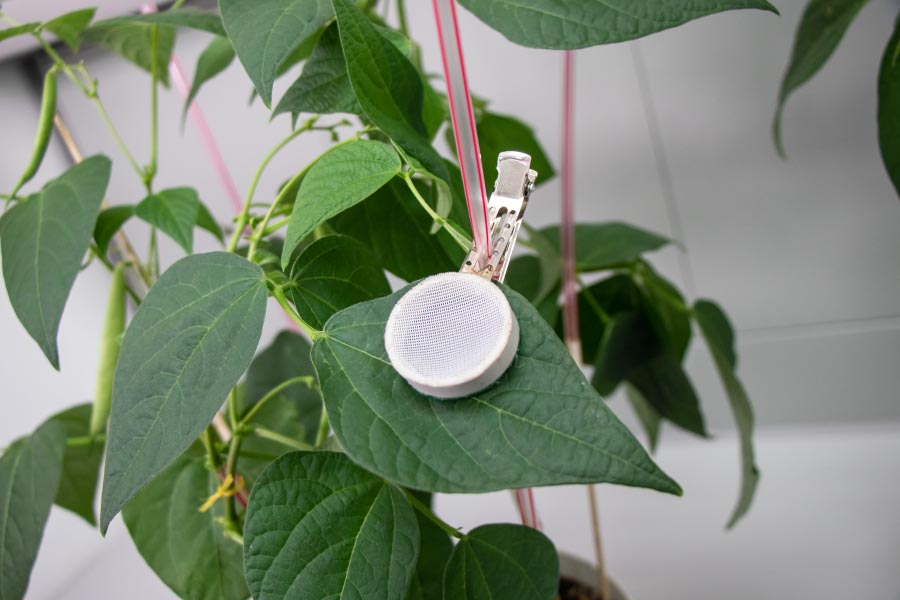
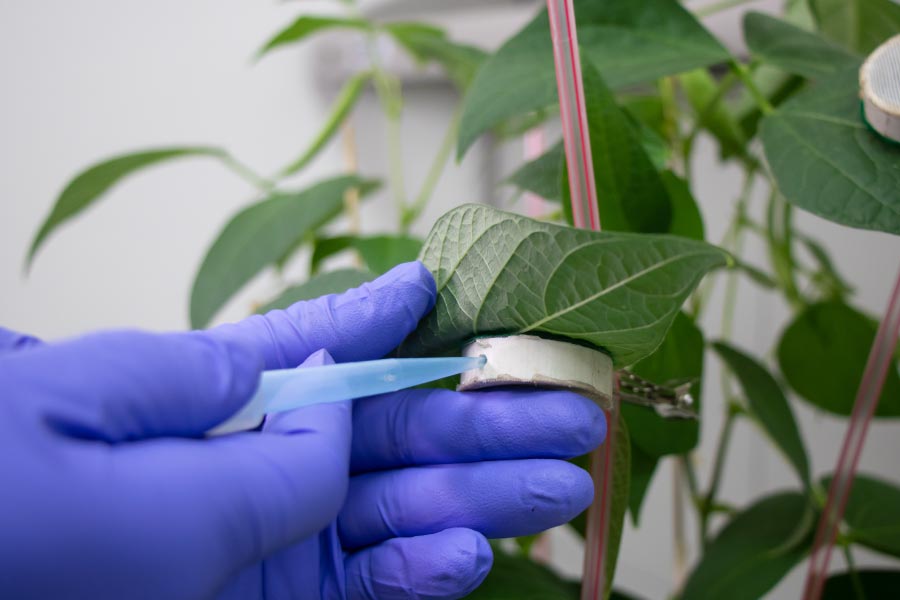
Agricultural Microbiology
The Network has technical capacities to characterize, identify and evaluate microorganisms of agricultural importance. The network includes a bio-input quality control area registered with Instituto Colombiano Agropecuario ICA [the Colombian Agricultural Institute], which offers more than 28 registered techniques for the quality analysis of biopesticides and biological inoculants within its portfolio.
It has specialized spaces for working with bacteria, fungi, viruses, and nematodes. In addition, it has areas with controlled conditions for the assembly of bioassays (temperature, humidity, photoperiod, and UV-B light).
This network includes the collections of microorganisms of interest for biofertilizers and biological control of the germplasm bank of the Colombian Nation. The microorganism accessions that are of interest for research can be requested at the following email: recursosbiologicos@agrosavia.co
The Network of Agricultural Microbiology Laboratories has 12 laboratories in different research centers nationwide.
Available services
- Microbiological quality control of organic fertilizers.
- Indicators for the microbiological quality of soils.
- Quality control of bio-inputs (area registered with ICA), including microbiological, physicochemical, and biological analyses.
- Quality control of biopesticides based on sporulated bacteria, biocontrol fungi, and entomopathogenic viruses.
- Quality control of biological inoculants.
Techniques Registered before ICA
| Analysis | Description |
|---|---|
| Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi |
Determination of the infection percentage of arbuscular mycorrhizae in roots, isolation, and quantification of spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. |
|
Biological inoculants |
Isolation and quantification of Colony Forming Units (CFU) of Azotobacter sp; isolation and quantification of Colony Forming Units (CFU) of rhizobia cells; determination of microbiological purity; evaluation of the biological activity of a biological inoculant under greenhouse conditions. |
| Microorganism-based biopesticides (microbiological tests) |
Contaminants content (bacteria, molds, and yeasts), germination of conidia of fungal biopesticides.
Active ingredient count (CFU) by plate count; active ingredient count (fungi and nucleopolyhedrovirus) using a Neubauer chamber.
|
| Microorganism-based biopesticides (biological tests) | Evaluation of the antagonism of microbial agents based on Trichoderma sp. and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; evaluation of the biological activity of granuloviruses and nucleopolyhedroviruses for the control of different insect pests; evaluation of the biological activity of entomopathogenic fungi under laboratory conditions. |
| Biopesticides and biological inoculants (physiochemical tests) | Moisture content, pH, particle size (Granulometry), disintegration, wettability, and density. |
| Soil microbiology | Count of presumptive nitrogen-fixing bacteria; count of presumptive phosphorus solubilizing bacteria; count of aerobic mesophilic bacteria, total fungi, and actinomycetes. |
Image gallery











