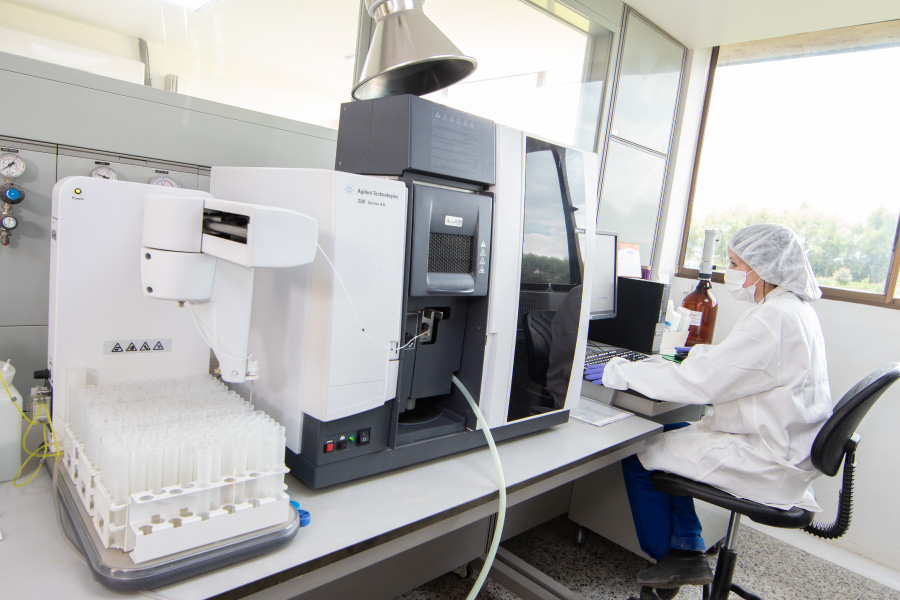
Analytical Chemistry
The Network of Analytical Chemistry Laboratories has the technical capacities to carry out soil fertility analysis, quality control, and nutritional determination in materials of agricultural importance, such as plant tissue, organic fertilizers, irrigation water, animal feed, and other foods, such as meat, fruits, panela, and cocoa.
This network has the technical capacity to carry out soil fertility analysis, determination of nutrient content in plant tissue, compositional quality control of animal feed, determination of heavy metals in the soil, water, and plant tissue for evaluation and control of agricultural safety, compositional evaluation for food quality control (milk, meat, fruits, panela, and cocoa), characterization of organic fertilizers under the Colombian Technical Standard NTC 5167 and diagnosis of water quality for irrigation for agricultural use.
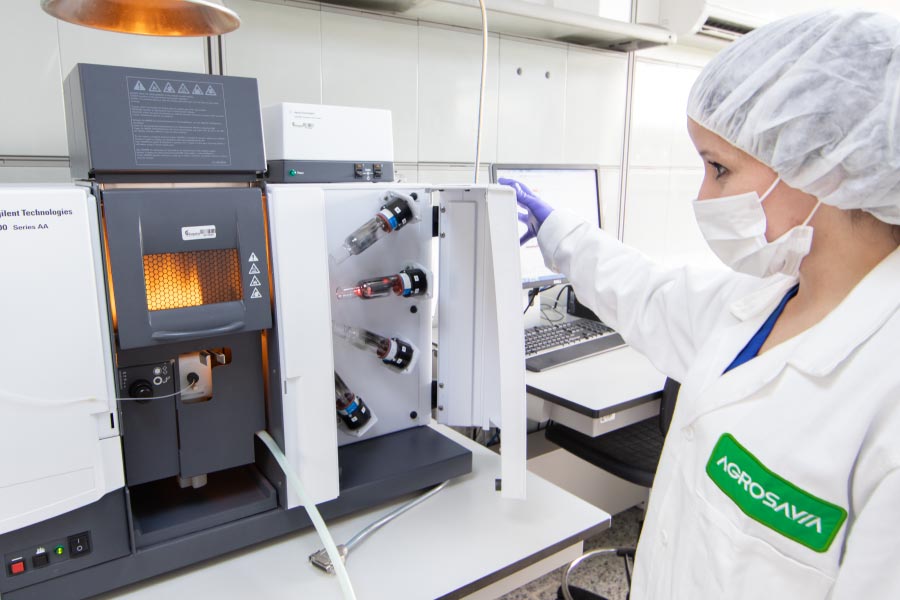
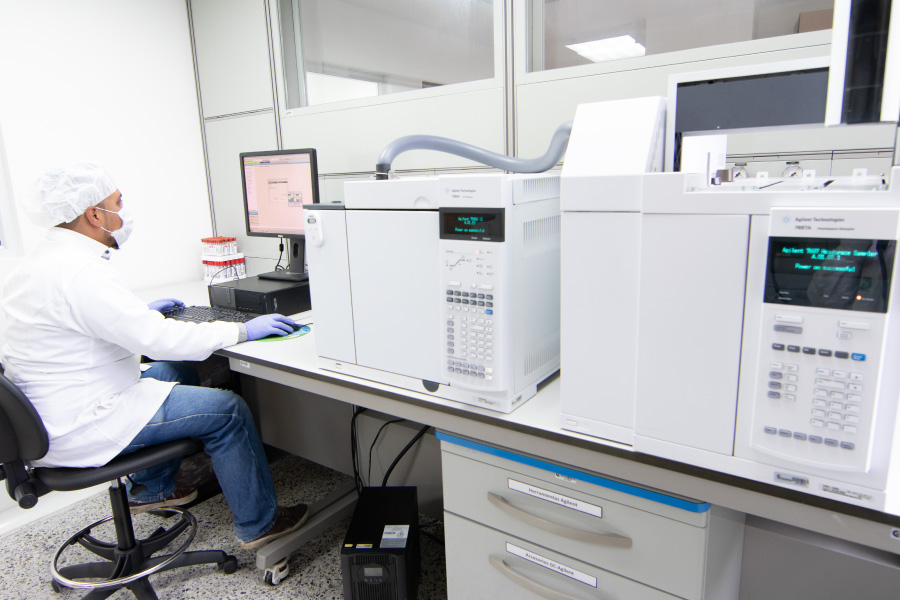
The laboratories have specialized areas of UV-VIS spectrophotometry, atomic absorption, inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry ICP-OES, elemental analysis by C, H, N, and S combustion, potentiometry, volumetry, liquid and gas chromatography, near-infrared (NIRS) and liquid-liquid and solid-liquid extractions.
In addition, the Network has accreditation in the International Standard ISO/IEC 17025 in the main parameters used in soils and technologies that allow the measurement of greenhouse gases, fruit respiration, acetylene reduction, and analysis of pesticide residues in food.
The Network of Analytical Chemistry Laboratories has six laboratories located in different research centers and an attached headquarters.
Available services
- Análisis de forrajes por NIRS
-
Soil fertility and chemical analysis of water for irrigation
- Nutritional analysis of plant material.
- Proximal analysis in animal feed by wet chemistry.
- Chemical analysis of organic fertilizers.
Soil
| Analysis | Description |
|---|---|
|
Chemical characterization |
Oxidizable organic matter (O.M), available phosphorus (P), pH, exchangeable calcium (Ca), exchangeable magnesium (Mg), exchangeable potassium (K), exchangeable sodium (Na), exchangeable acidity (Al, Al+H), electric conductivity (E.C), effective cation exchange capacity (ECEC) |
|
Fertility of Chemical complete |
Oxidizable organic matter (M.O), available phosphorus (P), pH, exchangeable calcium (Ca), exchangeable magnesium (Mg), exchangeable potassium (K), exchangeable sodium (Na), exchangeable acidity (Al, Al+H), effective cation exchange capacity (ECEC), available iron (Fe), available copper (Cu), available manganese (Mn), available zinc (Zn), available boron (B), electric conductivity (E.C) + sulfur (S) |
|
Particular per element |
Total nitrogen (N), exchangeable calcium (Ca), exchangeable magnesium (Mg), exchangeable potassium (K), exchangeable sodium (Na), available phosphorus (P), oxidizable organic matter (O.M), available iron (Fe), available copper (Cu), available manganese (Mn), available zinc (Zn), available sulfur (S), available boron (B), electric conductivity (E.C), real cationic exchange capacity (RCEC), pH. |
| Salinity complete |
pH, electric conductivity (E.C), real cationic exchange capacity (RCEC), exchangeable sodium (Na), percentage of exchangeable sodium (PES), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), soluble calcium (Ca2+), soluble magnesium (Mg2+), soluble potassium (K+), soluble sodium (Na+), carbonates (CO3=), bicarbonates (HCO3-), sulfates (SO4=), chlorides (Cl-), moisture saturation) |
|
Particular per Soluble element |
Soluble calcium (Ca2+), soluble magnesium (Mg2+), soluble potassium (K+), soluble sodium (Na+), carbonates (CO3=), bicarbonates (HCO3-), sulfates (SO4=), chlorides (Cl-), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), nitrates (N-NO3=) |
|
Heavy metals |
Pseudo-total: cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), chromium (Cr) |
|
Soil physics |
Hydraulic conductivity, apparent density (Da), true density (Dt), moisture retention (0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 3.0, and 15 bar), texture, liquid limit, and plastic limit, aggregate stability, total porosity, drainable porosity |
Water
| Analysis | Description |
|---|---|
|
Chemical irrigation complete |
pH, electric conductivity (E.C), total dissolved solids (TDS), hardness, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), carbonates (CO3=), bicarbonates (HCO3-), sulfates (SO4=), chlorides (Cl-), phosphates (PO4=), iron (Fe), boron (B) |
|
Particular per element |
pH, electric conductivity (E.C), total dissolved solids (TDS), hardness, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), carbonates (CO3=), bicarbonates (HCO3-), sulfates (SO4=), chlorides (Cl-), phosphates (PO4=), iron (Fe), boron (B), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), nitrates (NO3=), nitrites (NO2) |
|
Heavy metals |
Total: cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), chromium (Cr) |
Animal feed
| Analysis | Descripction |
|---|---|
|
Proximal analysis |
Moisture, ash, crude protein, ethereal extract, crude fiber |
|
Cellular wall analysis |
Acid Detergent Fiber (ADF), Neutral Detergent Fiber (NDF), Cellulose, Lignin |
|
Protein analysis |
Cornell fractionation: Soluble fraction (B1+A), A fraction (NNP), B1 fraction (true protein), insoluble fraction (B2+B3+C), B2 fraction, B3 fraction (NDIN nitrogen), C fraction (ADIN nitrogen) |
|
Biological trials |
Animal type production phase: In situ digestibility of dry matter in bovines |
Plant tissue
| Analysis | Description |
|---|---|
|
Complete |
Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), copper (Cu), sulfur (S), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), and boron (B). |
|
Particular per element |
Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), copper (Cu), sulfur (S), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), cobalt (Co), and chlorides (Cl-). |
|
Heavy metals |
Cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), lead (Pb)) |
Image gallery














